Today, we are constantly tapping, scrolling, clicking, using our hands, fingers, and thumbs on smartphones, tablets, computers, etc. Constant repetitive use has increased the development of carpal tunnel syndrome. If tingling, numbness, soreness, or electrical sensations have begun to develop in the hands, especially the index finger, thumb, or palm, carpal tunnel prevention measures can help before it becomes severe.
Pinched Nerve
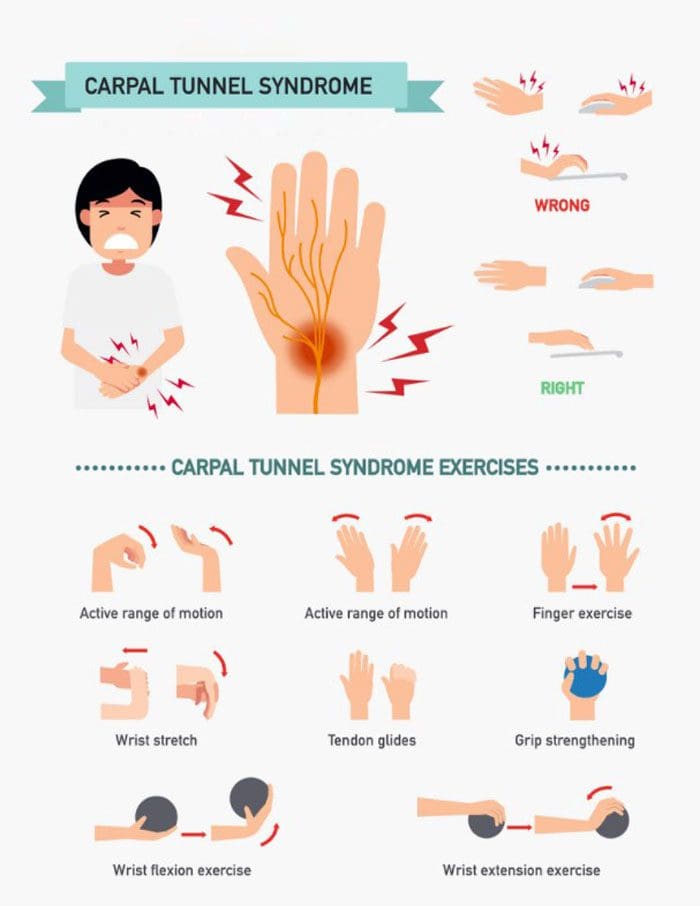
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the medical terminology for a pinched nerve. It is the median nerve that passes through the narrow carpal tunnel passageway of ligaments and bones at the base of the hand. This tunnel houses the median nerve and the tendons that allow the fingers to bend. The median nerve generates physical sensation in the index, middle, ring finger, and palm near the thumb. Compression of the nerve or inflammation can cause tingling, numbness, and pain in any and/or all of the hand areas. It can also cause the fingers to bend awkwardly; however, this symptom develops over time. There are so many different causes of carpal tunnel syndrome that it is almost impossible to avoid with the constant overuse/repetition of the hands.
- Work - tasks, typing, mouse use, writing, scanning, etc.
- School
- Injury
Doctors recommended approach for carpal tunnel prevention is to take action at the first sign/symptom. The most effective preventative measures include:
Take Frequent Hand Breaks
At work, school, or when doing any repetitive hand movements like:
- Typing
- Using a computer mouse - moving, clicking, using the scrolling wheel, etc.
- Writing
- Cooking - chopping, slicing, mixing, squeezing, etc.
- Drawing
- Make sure to take frequent breaks from the motion.
Carpal tunnel is more likely to develop if the nerves and muscles are overused for a long time without stopping. When focused on a task, we often don’t realize how the repetitive motions cause strain until a sting or pinch makes us stop. Taking a hand break is essential to give the muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves time to relax and stay loose. The break only has to be a few minutes to be effective.
Repetitive Movements and Proper Hand Form/Posture
Repetitive hand or wrist motions in everyday activities sometimes cannot be helped. It is recommended to try to switch hands when performing the task, space it out over the day, take frequent breaks, stretch, and gently shake out the hands throughout the day. Make sure any pressure on the hands or wrists is as light as possible and evenly distributed. Keep the wrists straight or slightly bent and use light tools if possible. Proper posture is crucial for carpal tunnel prevention. Many individuals don’t realize the back, neck, and wrists are intricately connected. Poor posture like hunching over the computer, shoulders rolled forward, and forward neck posture can cause the nerves and muscles of the arm to become compressed, causing tingling, numbing, pain symptoms because they’re not properly aligned. The compression can run down the arms and affect the wrists and hands as well.
Carpal Tunnel Prevention Supportive Accessories
It is also recommended to consider integrating supportive accessories, like ergonomic keyboards, mice, wrist splints, keypad cushions, etc. These tools can support the body and keep the wrists and hands healthy, comfortable, and pain-free. Wrist splints can help by keeping the wrist in a straight, neutral position without thinking about it. This reduces stress on the area and absorbs the pressure of everyday tasks on the carpal tunnel and median nerve. Individuals can also wear the splint at night to support and train the wrist to stay straight throughout the day. Taking action before the symptoms become severe is highly recommended. Talk to a chiropractor or physical therapist for exercises, stretches, and general tips to help with carpal tunnel prevention.
Body Composition
A Snack and A Meal
Without proper planning, the calories an individual consumes from snacks can add up. A recent survey found that snacking contributes 586 calories for men and 421 calories for women per day. Weight loss, weight gain, and weight maintenance come down to calories in vs. calories out.
- Eating snacks that are too high in calories or snacking too much can disrupt and derail health goals.
- It’s essential to know what a snack consists of, what to look for on a label, and how to plan.
- Snacks come in a range of calories, depending on individual goals.
- For many, 100-200 calories are recommended for snacks.
- Individuals that need increased calories may require a higher calorie snack.
- The number of snacks eaten per day depends on individual needs and goals.
- It’s best to plan and factor snacks into the overall meal plan to avoid overeating.
- Be sure to check labels and measure out snack portions.
The information herein is not intended to replace a
one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional, licensed
physician, and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make your own health
care decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified health
care professional. Our information scope is limited to
chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health
issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and
present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of
disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of
practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health &
wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of
the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights
cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and support, directly
or indirectly, our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has made a reasonable
attempt to provide supportive citations and has identified the relevant
research study or studies supporting our posts. We
provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards
and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an
additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or
treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above,
please feel free to ask Dr. Alex
Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900.
Dr.
Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN*
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
References
LeBlanc, Kim Edward, and Wayne Cestia. “Carpal tunnel syndrome.” American family physician vol. 83,8 (2011): 952-8.
Page, Matthew J et al. “Splinting for carpal tunnel syndrome.” The Cochrane database of systematic reviews vol. 2012,7 CD010003. 11 Jul. 2012, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010003
Shiri, Rahman, and Kobra Falah-Hassani. “Computer use and carpal tunnel syndrome: A meta-analysis.” Journal of the neurological sciences vol. 349,1-2 (2015): 15-9. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2014.12.037




