The body has around 1,000 ligaments that connect bones and joints. Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that support joint mobility and stabilize the muscles and bones. An injury to one or more ligaments can cause inflammation, swelling, discomfort, and instability. The PCL refers to the posterior cruciate ligament that runs along the back of the knee joint. This ligament connects the femur/thigh bone to the tibia/shinbone. Anyone can suffer from an injury to the posterior cruciate ligament. It can be caused by the knee hitting a dashboard in an automobile collision, a worker twisting or falling on a bent knee or a sports contact injury. The Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic Team provide soft tissue work, trigger point therapy, and targeted non-surgical treatment through advanced therapy methods and technologies.
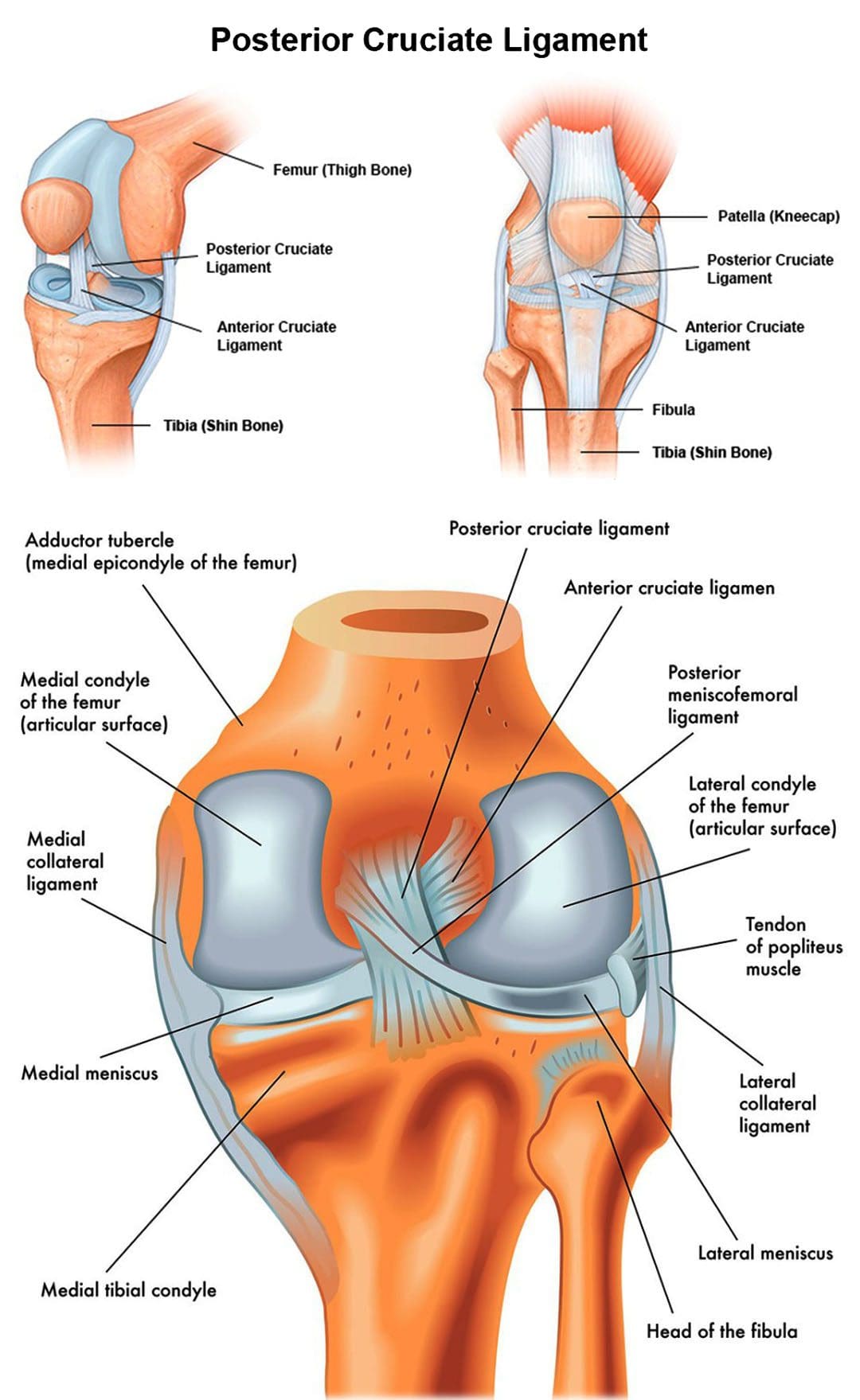 Posterior Cruciate Ligament
Posterior Cruciate Ligament
The posterior cruciate ligament - PCL is located inside the knee, just behind the anterior cruciate ligament - ACL. It is one of several ligaments that connect the femur/thighbone to the tibia/shinbone. The posterior cruciate ligament keeps the tibia from moving backward.
Injury
Posterior cruciate ligament injuries are far less common than ACL - anterior cruciate tears. PCL injuries make up less than 20% of all knee ligament injuries. It is more common for PCL tears to occur with other ligament injuries. A PCL injury can cause mild, moderate, or severe damage and is rated into four different categories:
Grade I
- A partial tear is present in the ligament.
Grade II
- There is a partial tear.
- The ligament can feel loose.
Grade III
- The ligament is completely torn.
- The knee is unstable.
Grade IV
- The PCL is injured.
- Other knee ligaments are damaged.
Individuals with posterior cruciate ligament injuries can have short or long-term symptoms. Typically, long-term symptoms occur when an injury slowly develops over time. In mild cases, individuals may still be able to walk, and their symptoms may be less noticeable. Common symptoms associated with PCL injuries include:
- Difficulty placing weight on the injured knee.
- Stiffness.
- Walking difficulties.
- Difficulty descending stairs.
- A wobbly sensation inside the knee.
- Inflammation and swelling can be mild to severe.
- Knee pain.
- Pain that worsens over time.
- Over time, tears could lead to the development of osteoarthritis.
There is an increased risk of extensive damage and chronic pain conditions if left untreated.
Chiropractic Care
The continued participation in work or activity following a mild injury is the primary reason individuals undergo therapy, injections, or surgical repairs. Knee injuries need immediate attention to prevent worsening or further damage. A chiropractor will examine the knee, check the range of motion and ask about symptoms. They may request imaging tests to determine the extent of the damage. These tests may include the following:
- X-rays.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- CT scan.
During the physical examination, they will check all the structures of the injured knee and compare them to the non-injured knee. The wounded knee may appear to sag backward when bent or could slide back too far, specifically when beyond a 90-degree angle. Treatment depends on the severity of the injury. Common treatments include:
Crutches
- Crutches may be recommended to limit the weight placed on the knee.
Knee Brace
- A special brace can address instability and help prevent the tibia bone from sagging backward.
- Gravity tends to pull the bone backward when lying down.
Chiropractic and Physical Therapy
- As the swelling goes down, a carefully personalized rehabilitation program can begin.
- A chiropractic regimen will reset and retrain the ligament.
- Massage therapy will minimize scar tissue and increase circulation.
- Specific exercises will stabilize the knee, restore function, and strengthen the leg muscles that support it.
- Strengthening the muscles in the front of the thigh/quadriceps is a key factor in a successful recovery.
Surgery
- In severe cases, surgery may be necessary for full rehabilitation.
- Knee arthroscopy is performed to reconstruct the ligament.
- This procedure is less invasive compared to traditional surgical methods.
Recovery time varies from person to person. If the injury is mild, it may only take around ten days to heal. If surgery was needed, recovery could take about six to nine months. Full recovery typically requires 6 to 12 months.
Best Knee Injury Chiropractor
The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from a wide array of disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900.
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN*
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
References
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries. (https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/posterior-cruciate-ligament-injuries) Accessed 7/26/21.
Bedi A, Musahl V, Cowan JB. Management of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries: An Evidence-Based Review. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgery. 2016 May;24(5):277-89. Accessed 7/26/21.
Lu, Cheng-Chang, et al. “Twelve Weeks of a Staged Balance and Strength Training Program Improves Muscle Strength, Proprioception, and Clinical Function in Patients with Isolated Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries.” International journal of environmental research and public health vol. 18,23 12849. 6 Dec. 2021, doi:10.3390/ijerph182312849
Pierce, Casey M et al. “Posterior cruciate ligament tears: functional and postoperative rehabilitation.” Knee surgery, sports traumatology, arthroscopy: official journal of the ESSKA vol. 21,5 (2013): 1071-84. doi:10.1007/s00167-012-1970-1
Schüttler, K F et al. “Verletzungen des hinteren Kreuzbands” [Posterior cruciate ligament injuries]. Der Unfallchirurg vol. 120,1 (2017): 55-68. doi:10.1007/s00113-016-0292-z
Zsidai, Bálint, et al. “Different injury patterns exist among patients undergoing operative treatment of isolated PCL, combined PCL/ACL, and isolated ACL injuries: a study from the Swedish National Knee Ligament Registry.” Knee surgery, sports traumatology, arthroscopy: official journal of the ESSKA vol. 30,10 (2022): 3451-3460. doi:10.1007/s00167-022-06948-x




