With so much at stake, our bodies have developed a complex self-defense system to protect the spinal cord and its critical two-way sensory information flow. As the body’s nerve center the spinal cord controls almost all voluntary and involuntary movements throughout the torso, arms, and legs. It also receives sensory input from the torso and limbs. The spinal cord plays a critical role and needs to be defended. The most prominent protection for the brain is the skull, for the spinal cord, it is more complicated.
Self Defense
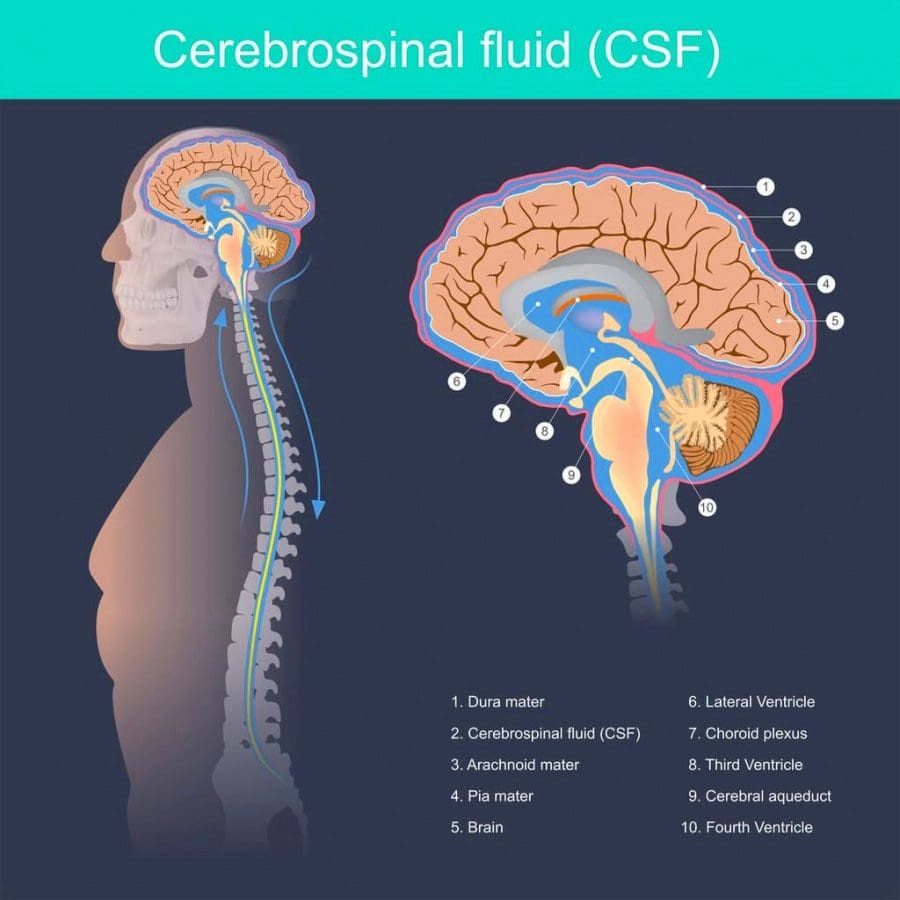
The spinal cord consists of a bunch of nerves. One of the self-defenses is the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that cushions and nourishes them. On the outside, the spinal cord is protected by the tube structure known as the meninges. Three-layered membranes make up the meninges, each with its own protective role:
- Pia mater
- Arachnoid mater
- Dura mater
Meninges
The meninges are three layers of membranes that encapsulate the spinal cord at the brainstem from the top to the bottom of the spine. The innermost layer is the pia mater and is attached directly to the spinal cord. It is made up of mostly collagen that has an elasticity that allows the cord to maintain its shape. Next comes the arachnoid mater and is the middle layer.Its primary role is to maintain the cerebrospinal fluid that fills the subarachnoid space between the pia and the arachnoid. A common condition known as arachnoiditis involves the arachnoid mater. It is a painful inflammation of the membrane that requires medical treatment. It can lead to disability if it is progressive.
Dura Mater
The outer layer is the dura mater and is the toughest. The dura rests on the arachnoid with a small amount of fluid in-between. The epidural space separates this membrane from the wall of the vertebral canal. Although it is tough, tears can occur. Tears can result from:- Injury
- Epidural injections
- Lumbar punctures
- Complications from spine surgery
Postural headaches are worse standing than sitting or laying down and can be severe are the most common symptom of spinal fluid leaks. But these tears typically heal quickly with bed rest.
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid is the clear liquid that fills the space between the pia and the arachnoid. It is made in the brain’s ventricles with its primary function to protect and nourish the spinal cord and brain. The fluid also removes waste products from the brain. The fluid also plays a role in helping doctors diagnose disease/s.
If a doctor suspects a severe infection or disorder of the central nervous system, they perform a lumbar puncture or spinal tap. The fluid can also contain evidence of inflammation or infection from waste products that the central nervous system discarded into the fluid. A doctor inserts a needle between two vertebrae in the lower back to remove a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid. The fluid is sent to the lab and analyzed. Lumbar punctures can be used to diagnose conditions like:
- Infectious brain and spinal diseases like meningitis and encephalitis
- Nervous system disorders like multiple sclerosis and Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Bleeding in/around the brain
- Brain tumors
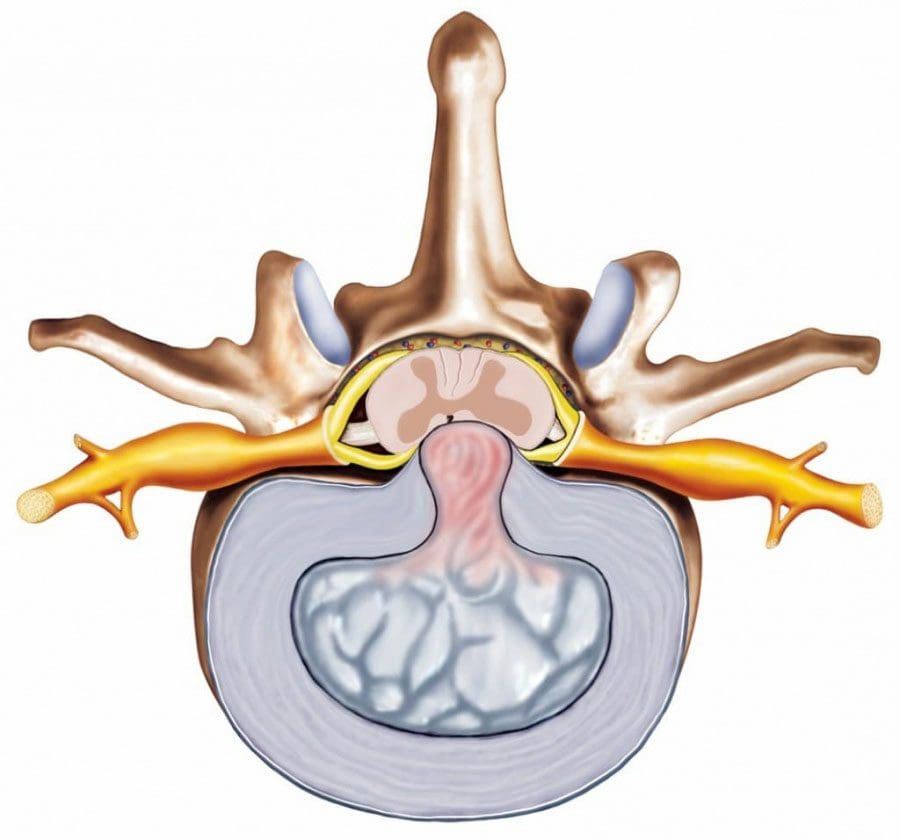
Vertebrae
There are 33 bones that make up the spine that forms a framework shaping the body and protecting the spine. In a healthy spine, the neck vertebrae curve slightly inward called lordosis, while the middle vertebrae curves outward called kyphosis before meeting the low vertebrae curved inward. This makes the spinal cord flexible and balanced.Each vertebra has a complex shape with a precise configuration determined by the location in the spine. Many conditions of the vertebrae involve nerves that get pinched/compressed as they exit the spine. Pinched nerves usually result from bone spurs on the vertebrae that crowd the canal and from herniated discs.
Intervertebral Discs
The intervertebral discs are the spine’s shock absorbers. They fill the space between two vertebrae with no direct contact. The endplates of each are coated with protective cartilage which anchors the discs in place. The gel substance part of each disc is called the nucleus pulposus. The tough cover known as the annulus fibrosus wraps around each disc to protect and shape it. There are no blood vessels in the discs and are nourished by the endplates of the vertebrae.
Herniated discs are the most common disc-related condition. When a disc herniates, the annulus fibrosus tears. The tear leaks out the protective gel to bulge out into the spinal canal. With no room in the canal for anything but the spinal cord and spinal fluid, the gel puts pressure on the surrounding nerve/s and the spinal cord itself. This is called myelopathy when the spinal cord gets compressed. Non-surgical treatments are quite successful in healing herniated disc/s.
The spine’s self-defense is elaborate, effective, and complicated. Consult an experienced spine specialist/chiropractor who can produce the best results and benefits.