The microbiomes in our bodies are fascinating. They help our various organs function correctly, helping out our immune systems battle terrible stuff. They can tell us what we are doing to our bodies when we consume food. However, the microbiomes in our gut tell us a different story as we are going to discuss what does microbiomes do as it functions in our body as well as our gut.
The relationship between the gut microbiota and its host plays a crucial role in:
- immune system maturation
- food digestion
- drug metabolism
- detoxification
- vitamin production
- prevention of pathogenic bacterial adhesion
Why Don’t We All Have the Same Microbiome?
Whenever we are trying to live a healthy lifestyle, our bodies will go through so many changes. When we get rid of the bad stuff that is causing us problems and the beautiful thing start taking effect in what we put in our bodies. We, as humans, have different body structures and body types that are way different. Some people lose or gain weight differently. When other people exercises, they go at their own pace, and several factors influence the bacterial composition in taxa type and abundance. These factors include:
- host phenotype, such as age, gender, body mass index (BMI)
- lifestyle
- immune function
- geographical belonging and environmental factors
- use of antibiotics, drugs, and probiotics
- DIET
Manipulating the Microbiome: Key Terms
Here are some key terms to remember when we are talking about the microbiome.- Stability: resistance to change and the ability to maintain homeostasis.
- Resilience: capacity to return to homeostasis after disturbance.
- Diversity: DIVERSE microbiomes are more stable and more resilient (to antibiotics); more resistant to foreign invasion (pathogens).
- Relative Abundance: Even ‘good’ bacteria can be too abundant without balance from symbiotic species; the presence of ‘bad’ bacteria is not necessarily always harmful if enough ‘good’ are there to balance.
- Colonization Resistance: The capacity of the microbiome communities to resist new colonization by pathogens and other transients.
- This is a KEY factor for preventing GI infections; but also explains why probiotics are not always practical.
- Our COMMENSAL microbiome is our first line and of defense
- Microbial depletion: Infection; Antibiotics; Toxins/Chemicals; Stress
- Restore balance/” reseeding”: (the term “reinoculate” is not really correct) Probiotics; Fermented foods; Prebiotics/Polyphenols.
Advantages to DNA Testing
For many practitioners, measuring microorganism DNA allows for:
- Detection of a more diverse collection of microorganisms, (more genus and species, particularly anaerobic species)
- They can measure at the species and subspecies level
- They have a much better snapshot of dysbiosis and diversity
- Have better accuracy of results
- Much faster turnaround time and much less expensive
- Concept of “epigenetics.”
Important Groups
These are some of the microbiomes that are very functional to our bodies and what parts do they play.Commensals
This microbiome provides the host with essential nutrients and contains Aerobic and Anaerobic microbiomes.
- Aerobic (survives better in oxygenated environments; less prevalent in the colon, however, some are considered ‘obligate anaerobes’). They are:
- Lactobacillus
- Bifidobacterium
- Bacillus
- Anaerobic (more likely to be found colonizing the distal colon due to limited oxygen). They are:
- Clostridia
- Akkermansia
Lactobacillus and Bifidobacteria
These two are the most well-researched genus of bacteria. They are widely available in commercially available probiotic products.- Lactobacillus are:
- lactic-acid forming bacteria
- Form biofilms which allow surviving harsh/low pH conditions (stomach acid)
- Helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier
- Abundant in probiotics/fermented foods
- Bifidobacteria are:
- One of the first bacteria to colonize the gut after birth
- Aids in digestion, reducing inflammation, and stimulation of immune cells
Bacillus
These are spore-forming bacteria. They form spores in harsh environments which makes them more resilient, heat-stable, and have better viability in the gastric environment. But they may have better efficacy as probiotic therapy in SIBO population. These are in another category of commercially-produced probiotics beyond the standard Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
In the health world, known as “Soil Based Probiotics.” They are very prominent in the environment and their primary role in immunomodulation; stimulation of the immune system. They are a production of GALT-Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue and are known to be significant players in the production of B Vitamins and Vitamin K2 in the gut known as Bacillus subtilis
Clostridia
These are a major anaerobic group of commensals. They comprise 10% to >50% of the microbiome and are critical for the health of the gut barrier and intestinal lining, and barrier integrity. These are essential producers of butyrate (SCFA) and secondary bile acids. They also thrive on a high and diverse fiber diet, grape, and red wine polyphenols such as Blautia, Butyrivibrio, Eubacterium, Faecalibacterium prausnitizi, Roseburia, Ruminococcus, etc. However, there are usually no probiotic supplements to directly increase the abundance of clostridia.
Akkermansia
These microbiomes make up 1-3% of a healthy microbiome, and they help maintain the health and integrity of the mucosal barrier.
- Akkermansia muciniphila = mucin lover
Proteobacteria
This is a PHYLUM category of bacteria. This microbiome contains gram-negative and all bacteria that carries an LPS. This group includes plenty of beneficial bacteria but also contains several pathogens that tend to thrive in pro-inflammatory condition.
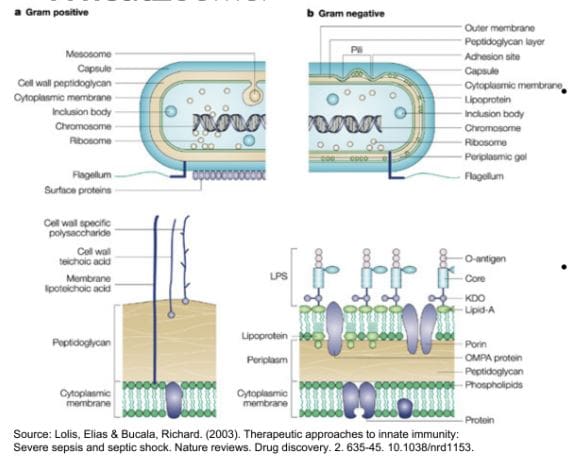
Gram (+) vs Gram (-) Bacteria
These two types of bacteria are in our bodies as they have very different functions that can either protect or disrupt our gut.
- Gram-Positive (+) contains:
- Peptidoglycan
- Lipoteichoic acid
- Gram-Negative (-) contains:
- LPS as a component of their cell wall
- LPS is a very powerful ENDOTOXIN- a known contributor to induce significant inflammation and potent immune response
- LPS antibodies are measured on Vibrant Wellness Wheat Zoomer/Intestinal Permeability Panel
LPS(Lipopolysaccharide)
In the last article, we mentioned them briefly, but here is a refresher on what theses microbes do. They are a fat/sugar molecule that lines the gram-negative bacteria inside the gut, and they protect those bacteria from bile salts. They are present inside the gut lumen under normal physiological conditions, and they usually should not enter the bloodstream. But if it does open in the blood then…
- 1) LPS antibodies are created-tagged as “non-self.”
- 2) Indication of intestinal permeability.
- 3) triggers multiple inflammatory cascades = ENDOTOXEMIA
- 4) Can help differentiate if leaky gut is happening between cells or through cells (or both), which are Transcellular vs. Paracellular pathways