Etiology of Sciatic Nerve Pain
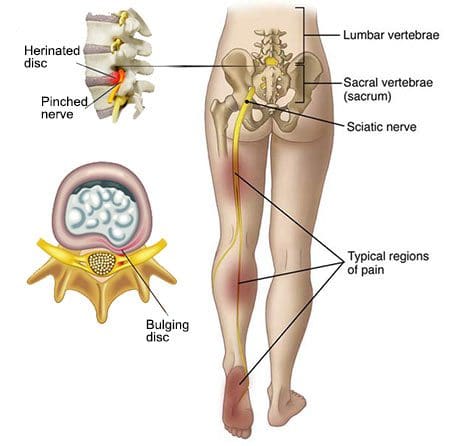
Sciatica, or sciatic nerve pain, is a collection of symptoms caused by the compression or impingement of the spinal cord and/or nerve roots, due to disk herniation, spinal health issues like osteoarthritis, spondylolisthesis, and spinal stenosis as well as intraspinal tumors and abscesses. Impingement or compression may typically occur along the spinal canal or intervertebral foramen. Health issues associated with the compression or impingement of the spinal cord and/or nerve roots may commonly occur in the lower back, pelvis, or buttocks.
Sciatica Symptoms
The common symptoms of sciatic nerve pain include pain and discomfort which radiates along the lower back, down the buttocks and posterior aspect of the leg, into the knee and foot. The painful symptoms may affect one or both lower extremities and it may occur with or without low back pain. The pain and discomfort are described as burning, lancinating, or stabbing. Other common symptoms of sciatica include tingling sensations and numbness anywhere along the length of the sciatic nerve, particularly in the lower extremities.
Coughing or the Valsalva maneuver, a specific way of breathing which increases pressure in the chest, may worsen sciatic nerve pain symptoms. Moreover, the compression or impingement of the spinal cord and nerve roots can cause sensory, motor, or reflex deficits, among other health issues. Symptoms of sciatica may depend on which nerves are affected based on the segmental level of the spine. By way of instance, an L5 to S1 disk herniation may affect the ankle jerk reflex while an L3 to L4 disk herniation may affect the knee jerk reflex.

Sciatica, or sciatic nerve pain, is a collection of symptoms rather than a single health issue, characterized by radiating pain, tingling sensations, and/or numbness which extends from the lower back and buttocks, down into the legs and feet. Sciatica is generally diagnosed through its symptoms and depending on the type of painful symptoms, a healthcare professional can safely and effective treat sciatic nerve pain. It's important for patients to understand the symptoms of sciatica in order to continue with a diagnosis and follow-up with the appropriate treatment option. - Dr. Alex Jimenez D.C., C.C.S.T. Insight
Healthcare professionals have determined that straight leg raising may aggravate pain and discomfort which radiates down the length of the leg when gradually raised above 60 degrees or less. According to numerous research studies, this outcome measure is sensitive to sciatic nerve pain. Painful symptoms radiating down the affected leg when the contralateral leg is lifted, also known as crossed straight leg raising, is more common for sciatica. Furthermore, sciatica can ultimately be diagnosed through a series of tests and evaluations.
The straight leg raise test can be performed while patients are sitting with their hip joints flexed at 90 degrees. Then, their leg is carefully raised until the knee is fully extended. If the patient has sciatica, the painful symptoms will most often manifest as the leg is extended. The slump test can be performed like the straight leg raise test, but while the patient is slumping with the thoracic and lumbar spine flexed as well as the neck flexed. The slump test is more accurate but less specific, for disk herniation than the straight leg raise test.
Sciatic Nerve Pain Diagnosis
Sciatica is commonly diagnosed through its characteristic, painful symptoms. Once sciatic nerve pain is diagnosed, healthcare professionals should test a patient's strength, sensations, and reflexes to determine any possible health issues. If painful symptoms persist for more than 6 weeks, or if there are neurologic deficits, imaging and electrodiagnostic studies should be performed. Structural and functional abnormalities which result in sciatica, such as spinal stenosis, can most accurately be diagnosed through MRI or CT scans.
Imaging and electrodiagnostic studies can help confirm the segmental level of the spinal cord and/or nerve root compression and/or impingement, which can exclude health issues that may mimic sciatica, such as polyneuropathy. These studies may help determine whether single or multiple regions of the spinal cord and/or nerve roots are being affected and whether the diagnosis correlates with MRI abnormalities. Abnormalities may not be obvious on imaging and electrodiagnostic studies for up to a few weeks after symptoms manifest.
Sciatica Treatment
Patients with sciatica, or sciatic nerve pain, can achieve relief from their painful symptoms through bed rest in a recumbent position with the head of the bed elevated about 30 degrees, also known as the semi-Fowler position. Treatment for low back pain can include nonopioid analgesics, such as NSAIDs and acetaminophen. Drugs and/or medications which decrease neuropathic pain, such as gabapentin or other anticonvulsants and low-dose tricyclic antidepressants, may also help relieve sciatic nerve pain, or sciatica, signs and symptoms.
Muscle spasm associated with low back pain or sciatica can be relieved through the utilization of heat or cold, physical therapy, and chiropractic care, among other alternative treatment options. Whether corticosteroids should be used to treat acute radicular pain remains controversial. Epidural corticosteroids can help achieve pain relief, however, these should not be utilized unless the patient's painful symptoms are severe or persistent. Many healthcare professionals may utilize oral corticosteroids for these special occasions.
Surgery for sciatic nerve pain, or sciatica, is only recommended for cauda equina syndrome or for unequivocal disk herniation along with the presence of muscular weakness, progressive neurologic deficit and/or intolerable, intractable pain which interferes with regular physical activities in an emotionally stable patient which has not decreased after 6 weeks of conservative treatments. The standard procedure for sciatica caused by disk herniation is through classic diskectomy with a limited laminotomy. If the disk herniation is localized, a microdiscectomy may be performed, where the skin incision and laminotomy are smaller. Chemonucleolysis, which uses an intradiscal injection of chymopapain, is no longer utilized to help treat sciatic nerve pain.
Sciatica is a collection of symptoms caused by the compression or impingement of the spinal cord and/or nerve roots. Understanding the symptoms of sciatic nerve pain is essential towards obtaining a diagnosis in order to follow up with the best treatment. The scope of our information is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal and nervous health issues as well as functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. To further discuss the subject matter above, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at 915-850-0900 .
Curated by Dr. Alex Jimenez
Additional Topic Discussion: Severe Sciatica
Back pain is one of the most prevalent causes of disability and missed days at work worldwide. Back pain attributes to the second most common reason for doctor office visits, outnumbered only by upper-respiratory infections. Approximately 80 percent of the population will experience back pain at least once throughout their life. Your spine is a complex structure made up of bones, joints, ligaments, and muscles, among other soft tissues. Injuries and/or aggravated conditions, such as herniated discs, can eventually lead to symptoms of sciatica, or sciatic nerve pain. Sports injuries or automobile accident injuries are often the most frequent cause of painful symptoms, however, sometimes the simplest of movements can have these results. Fortunately, alternative treatment options, such as chiropractic care, can help ease sciatic nerve pain, or sciatica, through the utilization of spinal adjustments and manual manipulations, ultimately improving pain relief.
Formulas for Methylation Support

XYMOGEN’s Exclusive Professional Formulas are available through select licensed health care professionals. The internet sale and discounting of XYMOGEN formulas are strictly prohibited.
Proudly, Dr. Alexander Jimenez makes XYMOGEN formulas available only to patients under our care.
Please call our office in order for us to assign a doctor consultation for immediate access.
If you are a patient of Injury Medical & Chiropractic Clinic, you may inquire about XYMOGEN by calling 915-850-0900.

For your convenience and review of the XYMOGEN products please review the following link.*XYMOGEN-Catalog-Download
* All of the above XYMOGEN policies remain strictly in force.




