Ataxia is a degenerative disease of the nervous system. Symptoms can mimic those of being inebriated/intoxicated, with slurred speech, stumbling, falling, and unable to maintain coordination. This comes from degeneration of the cerebellum, which is the part of the brain responsible for coordinating movement. It is a disease that affects people of all ages. However, age of symptom onset can vary, from childhood to late adulthood. Complications from the disease can be serious, even debilitating and life shortening.
Symptoms can vary from person to person, as well as, the type of Ataxia. Symptom onset and progression can vary as well. Symptoms can worsen slowly, over decades or quickly, over a few months. The common symptoms are lack of coordination, slurred speech, trouble eating, swallowing, eye movement abnormalities, motor skill deterioration, difficulty walking, gait abnormalities, tremors, and heart problems. People with Ataxia usually require wheelchairs, walkers, and/or scooters to aid in mobility.
Ataxia
The Loss Of Full Control Of Bodily Movements, Especially Gait
History Of Ataxia
- How long has it been present?
- Slow onset ➔ Degenerative disease?
- Acute onset ➔ Stroke?
- When does it occur?
- If worsened by walking on uneven surfaces, or with limited vision ➔ Sensory ataxia?
- Are there any coexisting symptoms?
- Vertigo, weakness, stiffness, cognitive changes, etc.
- Have others noticed this gait disturbance?
- If no, consider psychogenic cause
- Is the gait change explainable by physical problems such as pain or weakness?
- Antalgic gait, limp, etc.
Weakness
- Proximal muscle weakness ➔ Myopathy?
- Distal muscle weakness ➔ Neuropathy?
- UMN signs?
- LMN signs?
- Has the patient fallen? Or at risk for fall?
- Is ataxia limiting ADLs?
Balance
- Utilizes
- Vestibular system
- Cerebellar system
- Conscious proprioceptive information (joint position sense)
- Visual information
- Motor strength and coordination
Vestibular System
- Generally, if the problem lies in the vestibular system the patient will experience dizziness, possibly having vertigo or nystagmus
- Unable to walk a straight line
- When walking, will tend to veer to one side
Testing The Vestibular System
Fukuda Stepping Test
- Patient marches in place with eyes closed and arms raised to 90 degrees in front of them
- If they rotate more than 30 degrees = positive
- Patient will rotate toward the side of vestibular dysfunction
Rhomberg Test
- If patient sways a different direction every time their eyes are closed, this may indicate vestibular dysfunction
Cerebellar System
- Cerebellar gaits present with a wide-base and generally involve staggering and titubation
- Patient will have difficulty doing Rhomberg’s test with eyes open or closed, because they cannot stand with their feet together
- Afferent information helps make assessments about where the body is in space
- Ventral spinocerebellar tract
- Dorsal spinocerebellar tract
- Cuneocerebellar tract
- Olivocerebellar tract
- Efferent tracts carry responsive information to make adjustments to muscle tone and position to maintain balance
Testing The Cerebellar System
Piano-playing test & hand-patting test
- Both assess for dysdiadochokinesia
- Both tests, patient will have more difficulty moving the limb on the side of cerebellar dysfunction
Finger-to-nose test
- Patient may be hyper/hypo metric in movement
- Intention tremor may be reveled
Joint Position Sense
- Conscious proprioception may be diminished, especially in elderly patients and patients with neuropathy
Visual Information
- Patients with joint position sense losses often rely on visual information to help compensate.
- When visual input is removed or diminished these patient’s have exaggerated ataxia.
Motor Strength & Coordination
- If patient has reduced frontal lobe control they may end up with an apraxia of gait, where they have difficult with the volitional control of movement
- Extrapyramidal disorders such as Parkinson disease result in inability to control motor coordination
- Pelvic girdle muscle weakness due to a myopathy will produce an abnormal gait pattern
Commonly Seen Abnormal Gait Patterns
Circumduction gait
- Hemiplegia
- Often due to stroke
- Bilaterally (Diplegic gait), causes toe walking
- Typical gait of cerebral palsy patients
Festinating gait
- Small steps due to spasticity
- Often seen in Parkinson Disease
Myopathicgait(waddling)
- Seen in disorders of proximal muscle weakness
Steppage gait/Neuropathic gait
- Leg is lifted from the hip, without dorsiflexion at the ankle
- Often seen in patients with foot-drop due to a LMN lesion
- Wide-BasedCerebellargait
Gait Deviations
Dizziness
The Sensation Of Loss Of Balance
4 Main Types
- Vertigo
- Peripheral
- Central
- Pre-Syncope/Light-headedness
- Disequilibrium
- Other/Floating type
Peripheral Vertigo
- More common than central vertigo
- Due to damage to the inner ear or CN VIII
- Usually produces abnormal eye movements
- Nystagmus – May be horizontal or rotary
- Usually jerky in nature, with a fast and slow phase
- Named for the direction of the fast phase
- Vertigo usually worsens when patient looks to the side of the fast phase of nystagmus
- Severity of nystagmus usually correlates with severity of vertigo
- No other symptoms/signs of CNS dysfunction
- Patient may have nausea or difficulty walking, but only because of vestibular dysfunction
- Patient may also have hearing loss or tinnitus due if CN VIII or auditory mechanism function is damaged
- Typically the causes are benign, including
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
- Cervicogenic vertigo
- Acute labyrinthitis/Vestibular neuronitis
- Meniere’s Disease
- Perilymph fistula
- Acoustic Neuroma
Narrowing It Down
- If movement, particularly of the head/neck exacerbate vertigo, consider:
- BPPV
- Vertebrobasilar artery insufficiency
- Cervicogenic vertigo
- If noise brings on episodes, consider:
- Meniere’s disease
- Perilymph fistula
Vertigo Hx Questions
- Does your dizziness feel like you’re on an amusement park ride?
- Do you get nauseous when you’re dizzy?
- Are you spinning?
- Or is the world spinning?
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV/BPV)
- May develop spontaneously, especially in the elderly
- May arise due to head trauma
- Vertiginous episodes associated with specific movements:
- Looking at a high shelf (“top-shelf vertigo”)
- Bending over
- Rolling over in bed
- Onset of vertigo begins a few seconds after the movement, and resolves within about a minute
- Diagnostic test
- Dix-Hallpike Maneuver
- Treatment procedure
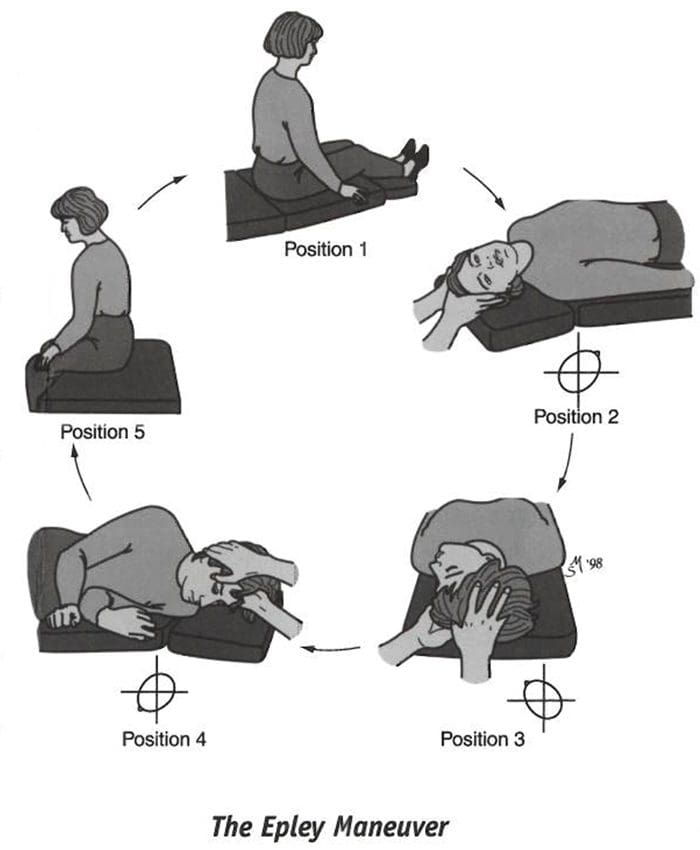
- Epley Maneuver
- Brandt-Daroff Exercises
- Can self resolve as crystals dissolve, but it may take months and new otoliths can become displaced
Cervicogenic Vertigo
- Occurs after head/neck injuries, but is not very common
- Usually accompanied by pain and/or joint restriction
- Usually vertigo and nystagmus will be less severe than in BPPV
- Vertigo begins with change in head position but does not subside as quickly as it does in BPPV
Vertebrobasilar Artery Insufficiency
- Occurs if the vertebral artery is compressed during head rotation/extension
- Onset of vertigo is delayed more than in BPPV or cervigogenic vertigo, because ischemia will take up to 15 seconds to occur
- Orthopedic test may help in evaluation
- Barré-Liéou Sign
- DeKlyn Test/Hallpike Maneuver
- Hautant test
- Underberg Test
- Vertebrobasilar After Functional Maneuver
Acute Labyrinthitis/ Vestibular Neuronitis
- Not well understood, but believed to be inflammatory in origin
- Follows viral infection or arise seemingly without cause
- Single, monophasic attack of vertigo
- Resolves in days to a few weeks and generally does not reoccur
Meniere’s Disease
- Increased pressure in the endolymph causes membrane ruptures and sudden mixture of endolymph and perilymph
- Episodes last 30 minutes to several hours, until equilibrium between the fluids is reached
- Over time, episodes damage vestibular and cochlear hair cells
- Low-pitch buzzing tinnitus
- Loss of hearing of low tones
Meniere’s Disease vs. Syndrome
- Meniere’s syndrome is when then symptoms of Meniere’s disease are found to be secondary to another condition, such as:
- Hypothyroidism
- Acoustic neuroma
- Superior semicircular canal dehiscence (SCDS)
- Perilymph fistula
- True Meniere’s disease is idiopathic
Perilymph Fistula
- Small leak due to trauma, especially barotrauma
- Can look very similar symptomatically to Meniere’s disease/syndrome
- Exacerbated by changes in pressure
- Airplane rides
- Driving uphill
- Hennebert’s sign
- Vertigo or nystagmus episode brought on by sealing pressure of the ear (such as by inserting an otoscope)
Central Vertigo
- Less common than peripheral vertigo
- Caused by damage to the processing centers of vestibular information in the brain stem and the cerebral cortex
- Typically “dizziness” is less severe than with peripheral vertigo
- Nystagmus
- Usually more severe than the description/patient’s complaint
- May go in multiple directions, including vertical
- May or may not have other CNS findings on examination
- No change in hearing expected
Causes Include:
- Cerebrovascular disease (such as transient ischemic attacks)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Arnold-Chiari Malformation
- Damage to caudal brainstem or vestibulocerebellum
- Migraine condition
Pre-Syncope Hx Qustions
- Does it feel like you’re going to pass out?
- Does the dizziness feel similar to when you stand up too fast?
Pre-Syncope
- “Light-headedness”
- CardiacOrigin
- Output disorders
- Arrhythmias
- Holter monitor testing
- Postural/Orthostatic hypotension
- May be secondary to other problems (diabetic neuropathy, adrenal hypofunction, Parkinsons, certain medications, etc.)
- Vasovagal episodes
- Slow heart rate with low blood pressure
- Often brought on by stress, anxiety or hyperventilation
- Migraine
- Due to cerebrovascular instability
- Blood sugar dysregulation
Disequilibrium Hx Questions
- Does the dizziness only occur when you’re on your feet?
- Does it get better if you touch/hold onto something?
Disequilibrium
- Common in the elderly
- Due to sensory deficits
- Gradual onset
- Worsened by reduced vision
- Dark
- Eyes closed
- Visual acuity losses
- Improved by touching a stationary object
- Subjective of dizziness often improves with a gait assistive device (cane, walker, etc.)
Other Causes
- Psychological stress
- Often patient will describe dizziness as “floating”
- Rule out hyperventilation and other types of dizziness
Sources
Blumenfeld, Hal. Neuroanatomy through Clinical Cases. Sinauer, 2002.Alexander G. Reeves, A. & Swenson, R. Disorders of the Nervous System. Dartmouth, 2004.