Other branches travel short distances up or down the spine to interact with neurons at other levels of the spinal cord. A branch can also turn into the posterior (dorsal) column white matter to connect with the brain. Spinal nerve systems that connect to the brain are contralateral, in that the right side of the body is connected to the left side of the brain and the left side of the body is connected to the right side of the brain.
Cranial nerves convey specific sense information from the head and neck directly to the brain. Whereas spinal information is contralateral, cranial nerve systems are for the most part ipsilateral, meaning that a cranial nerve on the right side of the head is connected to the right side of the brain. Some cranial nerves contain only sensory axons. Other cranial nerves have both sensory and motor axons, including the trigeminal, facial and glossopharyngeal. General senses of somatosensation for the face travel through the trigeminal system.
PATHWAYS
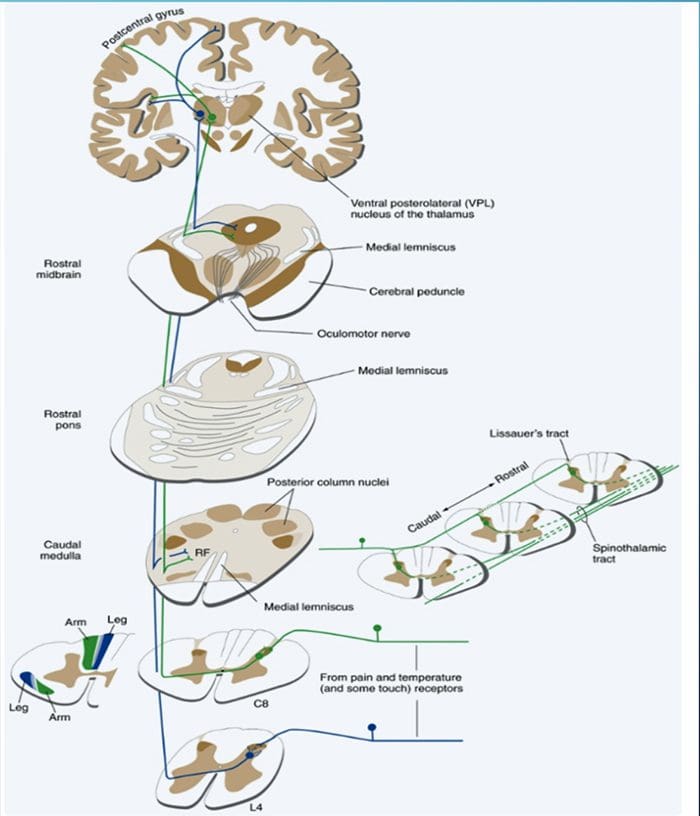
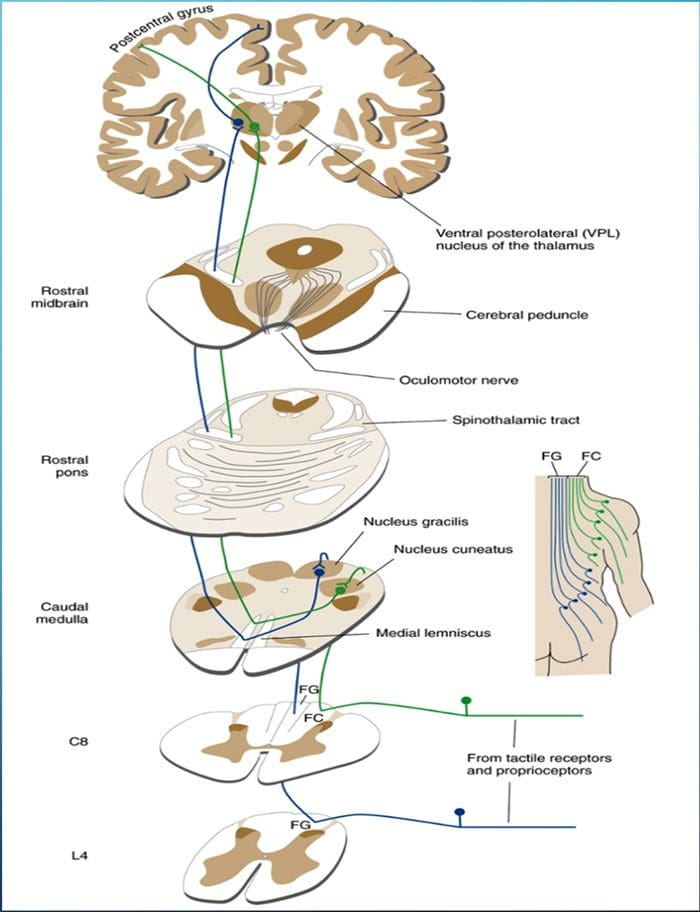
THE POSTERIOR COLUMN– MEDIAL LEMNISCUS SYSTEM CONVEYS INFORMATION ABOUT TOUCH AND LIMB POSITION
POSTERIOR COLUMN MEDIAL LEMNISCAL PATHWAY
- The term posterior column refers to the entire contents of a posterior funiculus, exclusive of its share of the propriospinal tract. The posterior columns consist mainly of ascending collaterals of large myelinated primary afferents carrying impulses from various kinds of mechanoreceptors (although substantial numbers of second-order fibers and unmyelinated fibers are also included). This has traditionally been considered the major pathway by which information from low-threshold cutaneous, joint, and muscle receptors reaches the cerebral cortex.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Touch & The Dorsal Columns-Medial Lemniscus
DAMAGE TO THE POSTERIOR COLUMN–MEDIAL LEMNISCUS SYSTEM CAUSES IMPAIRMENT OF PROPRIOCEPTION AND DISCRIMINATIVE TACTILE FUNCTIONS
“As might be expected from the types of afferents contained in the posterior columns, this pathway carries information important for the conscious appreciation of touch, pressure, and vibration and of joint position and movement. However, because input from cutaneous receptors also reaches the cortex by other routes, damage to the posterior columns causes impairment, but not abolition, of tactile perception. Complex discrimination tasks are more severely affected than is the simple detection of stimuli. Other functions, such as proprioception and kinesthesia, are classically considered to be totally lost after posterior column destruction. The result is a distinctive type of ataxia (incoordination of movement); the brain is unable to direct motor activity properly without sensory feedback about the current position of parts of the body. This ataxia is particularly pronounced when the patient’s eyes are closed, preventing visual compensation.”Given the role of the posterior column, the patient should be screened for any abnormalities regarding their sense of fine touch, vibration, barognosis, graphesthesia, stereognosis, kinaesthesia, two-point discrimination and conscious proprioception:
- A common way of testing for fine touch is to ask the patient to recognize common objects placed within a cloth using their touch.
- Vibration sense can be tested using a low pitched C128 tuning fork placed along a bony prominence of the desired corresponding spinal level(s) to be tested.
- Barognosis refers to the ability to determine the approximate weight of an object.
- Graphesthesia refers to the ability to recognize writing on the skin by touch. The practitioner can draw out a letter on the patients skin as a way of testing.
- Kinaesthesia refers to ones own sense of body motion (excluding equilibrium which is controlled in part by the inner ear) and is commonly tested using the subject’s ability to detect an externally imposed passive movement, or the ability to reposition a joint to a predetermined position.
- Proprioception is often assessed using the Rombergs test. This examination is based on the notion that a person requires at least two of the three following senses to maintain balance while standing: proprioception; vestibular function and vision. A patient who has a defect within their proprioceptive mechanism can still maintain balance by using vestibular function and vision. In the Romberg test, the patient is stood up and asked to close their eyes. A loss of balance is interpreted as a positive Romberg sign.
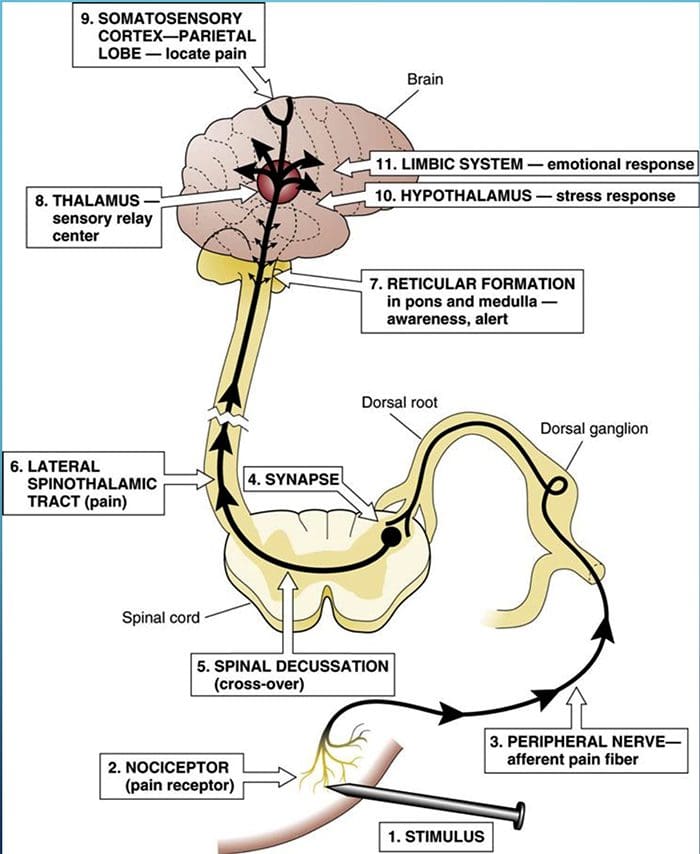
THE SPINOTHALAMIC TRACT CONVEYS INFORMATION ABOUT PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
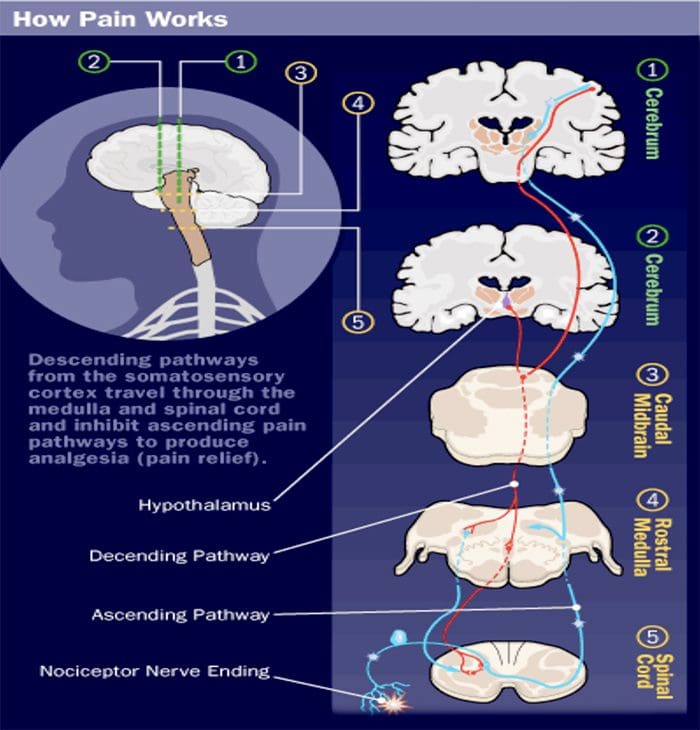
A GOOD BRAIN CAN MODULATE PAIN
SPINOTHALAMIC TRACT
- Pain is a complex sensation, in that a noxious stimulus leads not only to the perception of where it occurred but also to things such as a rapid increase in level of attention, emotional reactions, autonomic responses, and a greater likelihood that the event and its circumstances will be remembered. Corresponding to this complexity, multiple pathways convey nociceptive information rostrally from the spinal cord. One of them (the spinothalamic tract) is analogous to the posterior column–medial lemniscus pathway.
SPINOTHALAMIC TRACTS
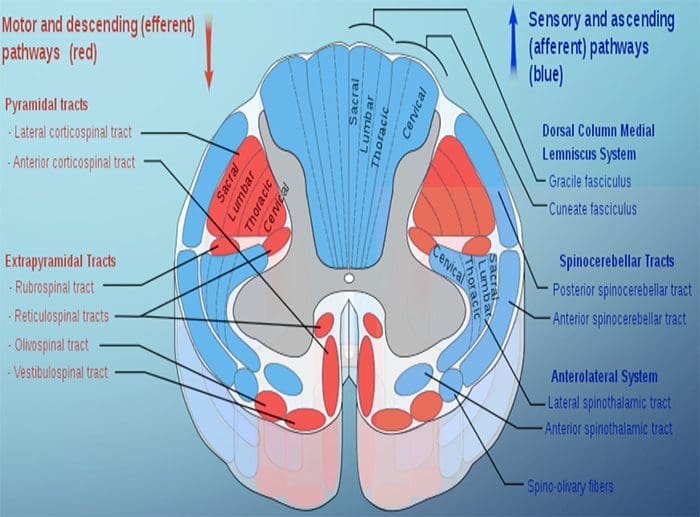
Two main parts of the Spinothalamic Tract (STT)
- Lateral Spinothalamic Tract
- Transmission of pain and temperature
- Anterior Spinothalamic Tract
- Transmission of crude touch and firm pressure
DAMAGE TO THE ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM CAUSES DIMINUTION OF PAIN AND TEMPERATURE SENSATIONS
Examination:
Given the role of the spinothalamic tract, the patient should be screened for any abnormalities regarding their sense of touch, pain, temperature, and pressure sensation.Screening for such abnormalities is commonly done using gentle pin pricks and cotton wool, to contrast between sharp and soft, following cutaneous sensory nerve root distributions. Hot and cold discrimination can be ascertained using the cold metal arm of a tuning fork, and a warm palm or heated object.
2 Minute Neuroscience: Pain & The Anterolateral System
HAUSER ET AL. FIBROMYALGIA, 2015
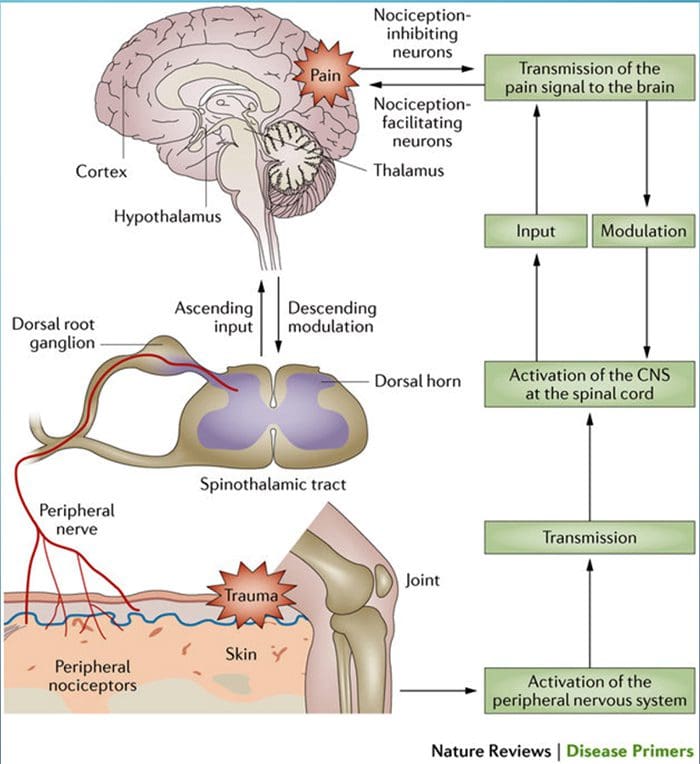
- “Pain processing and its modulation: Activation of peripheral pain receptors (also called nociceptors) by noxious stimuli generates signals that travel to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord via the dorsal root ganglion. From the dorsal horn, the signals are carried along the ascending pain pathway or the spinothalamic tract to the thalamus and the cortex. Pain can be controlled by nociception- inhibiting and nociception-facilitating neurons. Descending signals originating in the supraspinal centers can modulate activity in the dorsal horn by controlling spinal pain transmission. CNS, central nervous system.”
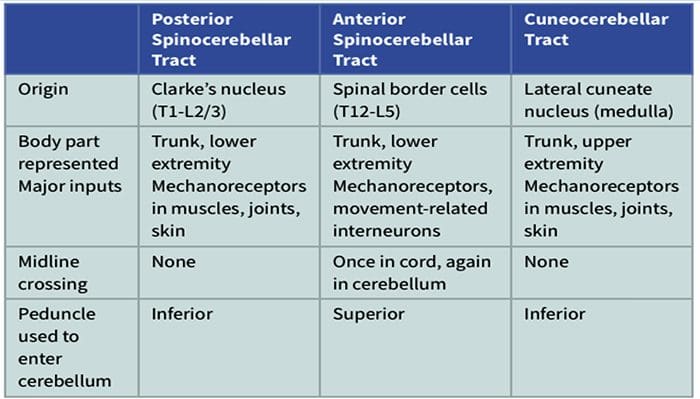
SPINAL INFORMATION REACHES THE CEREBELLUM BOTH DIRECTLY AND INDIRECTLY
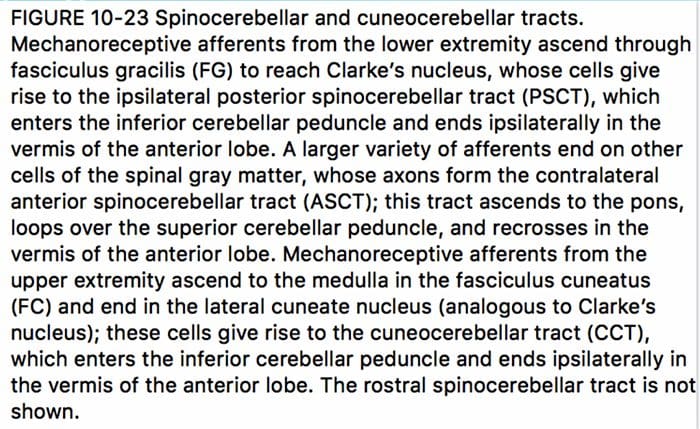
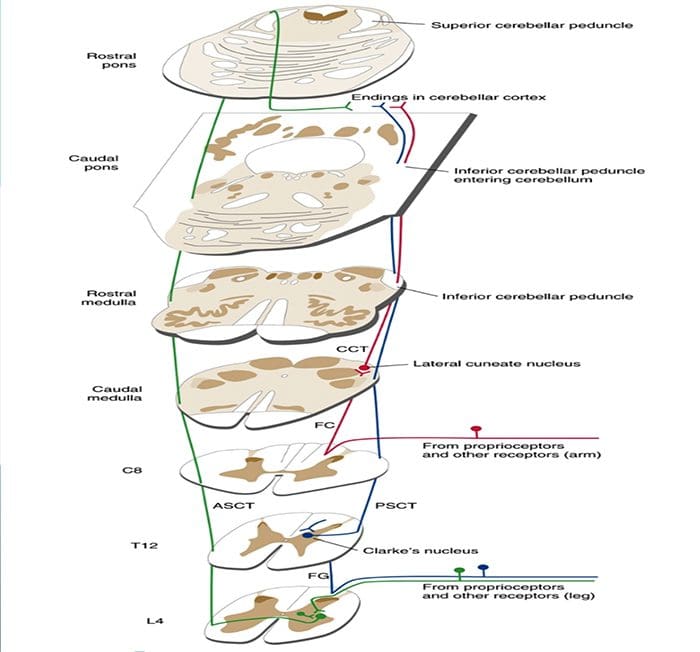
The spinal cord is an important source of information used by the cerebellum in the coordination of movement. This information reaches the cerebellar cortex and nuclei both directly, by way of spinocerebellar tracts, and indirectly, by way of relays in brainstem nuclei. A number of spinocerebellar tracts have been described, some representing the upper extremity and others the lower extremity. Only three have been well characterized.Ascending Tracts | Spinocerebellar Tract
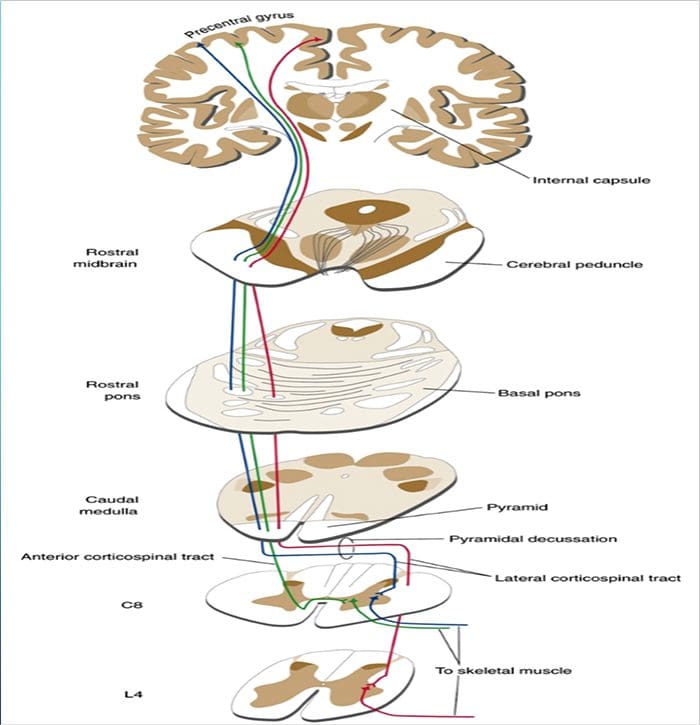
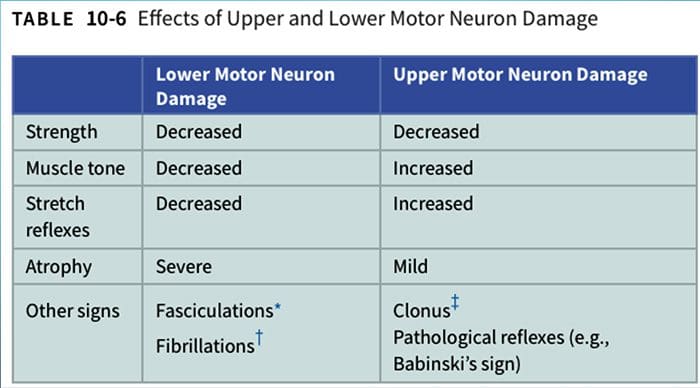
DESCENDING PATHWAYS INFLUENCE THE ACTIVITY OF LOWER MOTOR NEURONS
By RYAN CEDERMARK, DC DACNB RN BSN MSN