As the body grows older the ability to live life to the fullest can be difficult. Can using natural biologics help enhance the body’s natural ability to heal?
Natural Biologics
Though sometimes a necessary treatment option, surgical procedures can be the first line of treatment introduced to patients. Natural biologics is a less invasive alternative that can eliminate hospitalizations and expedite recovery. (Riham Mohamed Aly, 2020)
What Are They?
The body is born with components to initiate healing and recovery. These components include:
- Cells
- Cytokines
- Proteins
- Collagens
- Elastin
- Hyaluronic acid
At the time of birth, these components are in abundance but decrease as the body ages. This is why children recover from injuries quicker than adults. Recovery for adults can be slower from a decrease in these natural healing components. The objective of natural biologics treatments is to increase the healing components by reintroducing the body’s own components - autologous - or by bringing in new components - allogeneic - from a donor. (National Institutes of Health 2016) Choosing between the two options depends on an individual's age and health, as those who are older or in poor physical health may experience complications from inferior component amounts.
- Healing components derived from donor sources can show more promise, as treatments are usually acquired from discarded birth tissues at delivery.
- Birth tissues are rich in healing components, containing the most abundant collection of natural healing elements.
- It's important to note that there is no harm to the mother or the baby from the obtained tissue products.
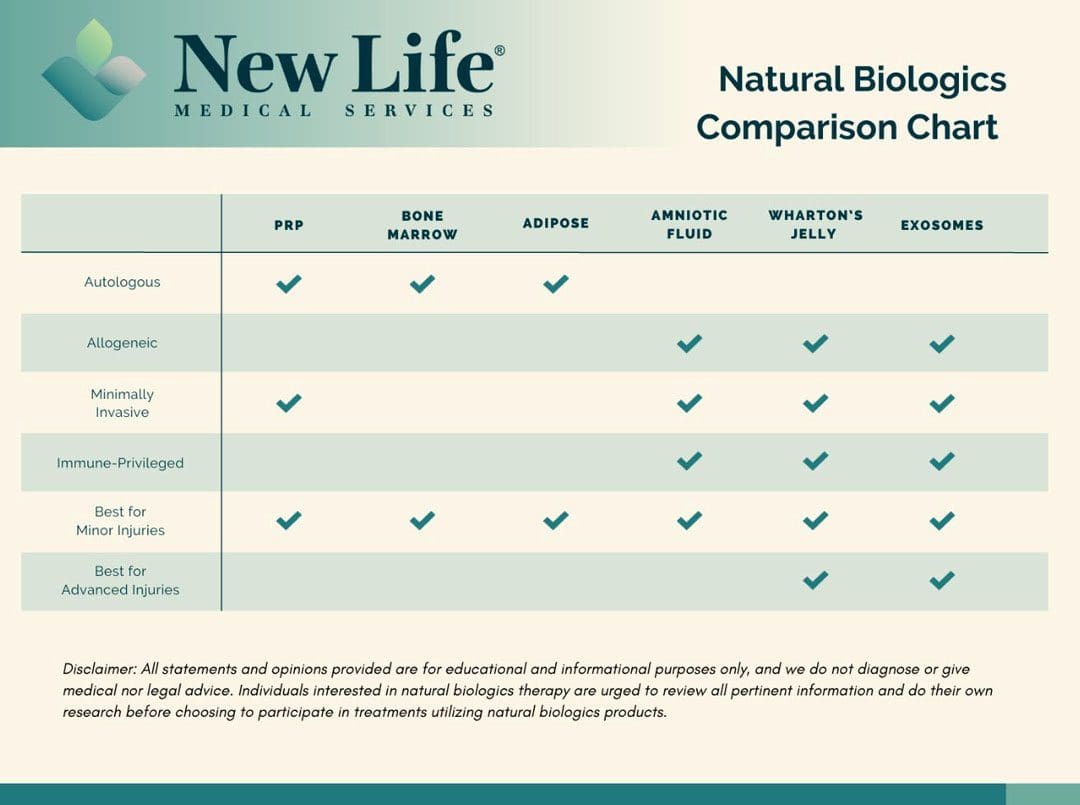
Autologous Treatment
Derived from the individual receiving the cell therapy. (Yun Qian, et al., 2017)
Platelet-Rich Plasma - PRP
- Platelet-rich plasma is cultivated by drawing an individual's blood and spinning it in a centrifuge to separate the plasma.
- The resulting liquid is reinjected into the injured area to generate a healing environment.
- This form of natural biologics is effective for individuals with minor injuries that can be repaired easily.
- This process is not as effective for older individuals who already have a reduction in natural healing components.
- Lifestyle factors such as smoking, unhealthy diet, and alcohol/substance abuse can decrease the effectiveness of PRP treatments.
Bone Marrow Aspirate
- This is an invasive, painful process that begins by putting a patient under anesthesia and drilling into the bone to extract the marrow. (American Cancer Society, 2023)
- Like PRP, success depends on the individual's age, health, and lifestyle.
- Invasive procedures like this have a higher probability of infection and require a long-term recovery period.
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
- Adipose tissue/fat treatments are collected through a procedure that resembles the process of liposuction.
- The procedure is done under general anesthesia and is an invasive process.
- Once the tissue is collected, the cells are separated and reinjected. (Loubna Mazini, et al. 2020)
- The treatment’s success depends on the individual's health, age, and lifestyle.
- There is more risk of infection when choosing this procedure and a long-term recovery period.
Allogeneic Treatment
Donor-based regenerative cells.
Amniotic Fluid Therapy
Amniotic fluid contains various growth factors, cytokines, and anti-inflammatory proteins that may promote tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and stimulate cellular regeneration. (Petra Klemmt. 2012)
- Collected at the time of birth, this therapy is an ideal treatment for individuals who have sustained injuries that affect day-to-day functionality.
- Physicians and clinicians are utilizing amniotic fluid therapy to treat many conditions, from orthopedic to wound care.
- Amniotic fluid is collected at the time of birth and is abundant with increased healing components compared to autologous sources.
- Amniotic fluid is immune-privileged (limits or suppresses immune response) and the risk of rejection is rare.
- These therapies are usually done in a physician’s office with minimal downtime after treatment.
Wharton’s Jelly
- Wharton’s jelly is derived from the umbilical cord at the time of birth and is primarily composed of a gel substance made up of hyaluronic acid and a network of collagen fibers.
- Its unique properties make it ideal for protecting and supporting the umbilical cord. (Vikram Sabapathy, et al., 2014)
- Believed to contain a population of mesenchymal stem cells that have the capacity to differentiate into various cell types, and other secreted growth factors and cytokines. (F. Gao, et al., 2016)
- It is considered the most valuable source to enhance the healing of various tissues, including bone, cartilage, skin, and nerve tissue.
- It is immune-privileged with little risk of rejection and minimal if any, recovery time after an in-office treatment.
Exosomes
- Exosomes are small, membrane-bound vesicles that play a role in intercellular communication within the body. (Carl Randall Harrell, et al., 2019)
- They contain a variety of bioactive molecules, including proteins, lipids, nucleic acids (like RNA), and signaling molecules.
- They serve as vehicles for transferring the signaling molecules from one cell to another, allowing cells to influence the behavior and function of neighboring or distant cells.
- They can be collected or isolated from various biological fluids and cell cultures through specialized techniques but are most robust when collected at birth.
- The exosomes within the umbilical cord are utilized for tissue repair and regeneration, signaling the cells to promote:
- Proliferation - increase in the number of cells through cell division.
- Differentiation - the transformation of unspecialized cells into specialized cells.
- Tissue healing in damaged or injured areas.
- Exosomes from the umbilical cord are immune-privileged with minimal risk of rejection.
- Treatments are ideal for increasing cell communication and initiating repair when paired with another source of allogeneic therapy like amniotic fluid or Wharton’s Jelly.
Choosing which natural biologics therapy is the best is different for everyone. When selecting a treatment, it is essential for individuals to consult their primary healthcare provider to determine which application will have optimal results.
Is Motion Key To Healing?
The information herein is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified healthcare professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional. Our information scope is limited to chiropractic, musculoskeletal, physical medicines, wellness, sensitive health issues, functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions. We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for the injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Our videos, posts, topics, subjects, and insights cover clinical matters, issues, and topics that relate to and directly or indirectly support our clinical scope of practice.* Our office has reasonably attempted to provide supportive citations and identified the relevant research study or studies supporting our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies available to regulatory boards and the public upon request.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how it may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to further discuss the subject matter above, please contact Dr. Alex Jimenez or contact us at
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, CCST, IFMCP*, CIFM*, ATN*
email: coach@elpasofunctionalmedicine.com
Licensed in: Texas & New Mexico*
References
Aly R. M. (2020). Current state of stem cell-based therapies: an overview. Stem cell investigation, 7, 8. https://doi.org/10.21037/sci-2020-001
National Institutes of Health. (2016). Stem Cell Basics.
Qian, Y., Han, Q., Chen, W., Song, J., Zhao, X., Ouyang, Y., Yuan, W., & Fan, C. (2017). Platelet-Rich Plasma Derived Growth Factors Contribute to Stem Cell Differentiation in Musculoskeletal Regeneration. Frontiers in chemistry, 5, 89. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00089
American Cancer Society. (2023). Types of Stem Cell and Bone Marrow Transplants.
Mazini, L., Rochette, L., Admou, B., Amal, S., & Malka, G. (2020). Hopes and Limits of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Wound Healing. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(4), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041306
Klemmt P. (2012). Application of amniotic fluid stem cells in basic science and tissue regeneration. Organogenesis, 8(3), 76. https://doi.org/10.4161/org.23023
Sabapathy, V., Sundaram, B., V M, S., Mankuzhy, P., & Kumar, S. (2014). Human Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells plasticity augments scar-free skin wound healing with hair growth. PloS one, 9(4), e93726. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093726
Gao, F., Chiu, S. M., Motan, D. A., Zhang, Z., Chen, L., Ji, H. L., Tse, H. F., Fu, Q. L., & Lian, Q. (2016). Mesenchymal stem cells and immunomodulation: current status and future prospects. Cell death & disease, 7(1), e2062. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.327
Harrell, C. R., Jovicic, N., Djonov, V., Arsenijevic, N., & Volarevic, V. (2019). Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles as New Remedies in the Therapy of Inflammatory Diseases. Cells, 8(12), 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121605




